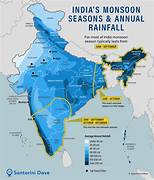
India is a land of diverse climate and geography, and rain plays a vital role in shaping the country’s ecosystem and economy. The monsoon season, which typically lasts from June to September, brings much-needed rainfall to the region. The rain-bearing winds from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal bring precipitation to different parts of the country, replenishing water sources, rejuvenating the environment, and reviving agricultural activities.
The southwest monsoon is the primary source of rainfall in India, accounting for a significant portion of the country’s annual precipitation. The monsoon rains are crucial for the country’s agricultural sector, as they support the growth of crops such as rice, wheat, and pulses. The timely arrival and distribution of monsoon rains are critical for the success of crops, and any deviations from the normal pattern can have significant impacts on agricultural production and food security.
Rain in India is not just limited to the monsoon season. The country experiences rainfall throughout the year, with different regions receiving precipitation at different times. The northeast monsoon, which occurs from October to December, brings rain to southern India, while the western disturbances bring winter rain to the northwestern parts of the country. These rainfall patterns are essential for sustaining agriculture, replenishing water sources, and maintaining ecological balance.
Despite the importance of rain, India also faces challenges related to excessive rainfall, such as floods and landslides. Heavy downpours can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and human settlements, leading to loss of life and property. On the other hand, deficient rainfall can lead to droughts, affecting agricultural production and water availability. Therefore, managing rainwater and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events are crucial for India’s economic and environmental sustainability.
Rainwater harvesting is an essential practice in India, given the country’s growing water scarcity challenges. Many parts of India face water shortages, and rainwater harvesting offers a sustainable solution to augment water supplies. By collecting and storing rainwater, households, communities, and institutions can reduce their dependence on groundwater and municipal water supplies, thereby contributing to water conservation efforts.
In conclusion, rain is a vital component of India’s climate and ecosystem, supporting agriculture, replenishing water sources, and sustaining ecological balance. While the country faces challenges related to excessive or deficient rainfall, effective management of rainwater and adaptation to changing weather patterns are essential for ensuring water security, food security, and environmental sustainability in India.
What is the primary source of rainfall in India?
The southwest monsoon is the primary source of rainfall in India, accounting for a significant portion of the country’s annual precipitation.
When does the monsoon season typically occur in India?
The monsoon season in India typically lasts from June to September.
Why is rain important for India’s agriculture?
Rain is crucial for India’s agriculture as it supports the growth of crops such as rice, wheat, and pulses, and replenishes water sources.
What are the impacts of deficient rainfall in India?
Deficient rainfall can lead to droughts, affecting agricultural production, water availability, and food security.
What are the impacts of excessive rainfall in India?
Excessive rainfall can cause floods and landslides, leading to loss of life and property, and damage to infrastructure and agriculture.
What is the role of rainwater harvesting in India?
Rainwater harvesting is an essential practice in India, helping to augment water supplies, reduce dependence on groundwater, and mitigate water scarcity.
Which regions of India receive rainfall during the northeast monsoon?
Southern India receives rainfall during the northeast monsoon, which occurs from October to December.
What are western disturbances, and how do they impact India?
Western disturbances are weather systems that bring winter rain to northwestern India, supporting the growth of crops such as wheat.
How does rain impact India’s ecosystem?
Rain plays a vital role in sustaining ecological balance in India, replenishing water sources, and supporting biodiversity.
Why is managing rainwater important for India’s sustainability?
Managing rainwater is crucial for India’s sustainability as it helps to ensure water security, mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events, and support agricultural production.